By focusing measurement on processes rather than functions, alignment and common focus across separate organizational units can be achieved (Hammer, 2007). This article discusses the concept of process performance measurement of the process management survey. Details on the survey (research design, sample, etc.) can be found here.
Implementing measures and taking corrective actions are operating precepts of process management (Melan, 1989). The results of the survey show that the concept of process performance measurement is partly established by organizations (see figures below). More than 40% of the surveyed firms state that process performance measurement is not implemented in the firm.
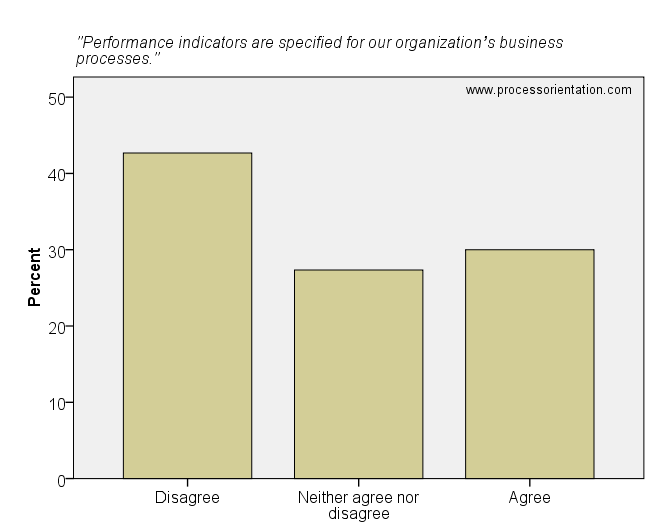
The item “Performance indicators are specified for our organization’s business processes” was rated by the firms in the sample as follows:
- 42,67%: Disagree
- 27,33%: Neither agree nor disagree
- 30,00%: Agree
Process performance indicators have to be derived from the process objectives which themselves have to be derived from business objectives. The results of the survey reveal that most of the firms which defined process performance indicators derived these indicators from enterprise goals and/or customer requirements. The item “Process performance indicators are derived from enterprise goals and/or from (internal) customer requirements” was rated by the firms in the sample as follows:
- 25,33%: No process performance indicators defined
- 10,00%: Disagree
- 22,00%: Neither agree nor disagree
- 42,67%: Agree
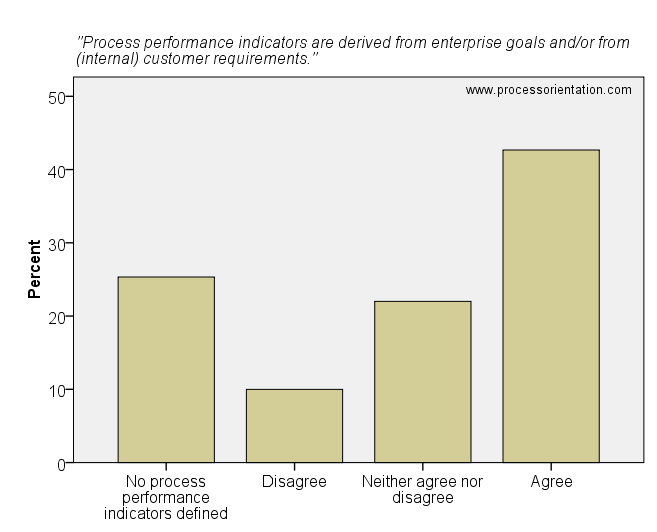
Process performance indicators are derived from enterprise goals and/or from (internal) customer requirements.
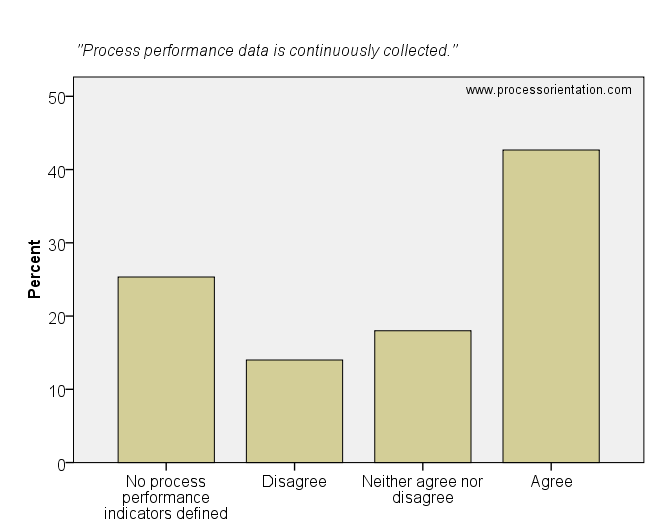
Process performance measurement only makes sense if performance indicators are calculated from process performance data which is collected continuously. Most firms which defined process performance indicators also continuously collect performance data. The item “Process performance data is continuously collected” was rated by the firms in the sample as follows:
- 25,33%: No process performance indicators defined
- 14,00%: Disagree
- 18,00%: Neither agree nor disagree
- 42,67%: Agree
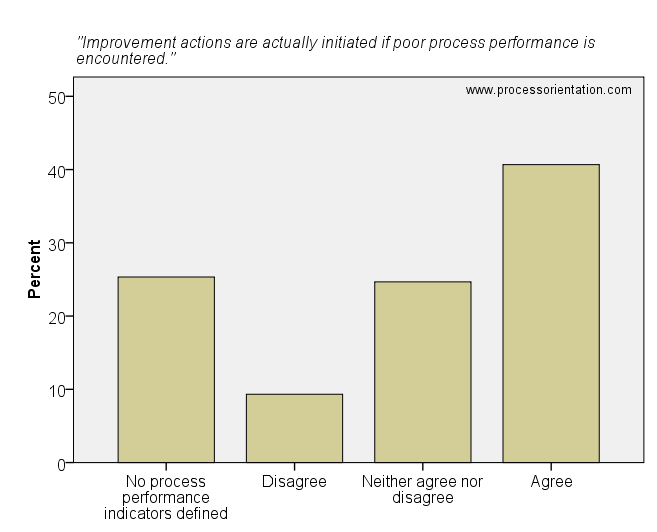
Measuring process performance without reacting on poor performance stresses resources, but does not lead to any improvements. Most firms which defined process performance indicators also initiate improvement actions if process performance is poor. The item “Improvement actions are actually initiated if poor process performance is encountered” was rated by the firms in the sample as follows:
- 25,33%: No process performance indicators defined
- 9,33%: Disagree
- 24,67%: Neither agree nor disagree
- 40,67%: Agree
Process workers who know the performance of the business process are able to timely react on bad performance. Most organizations which defined process performance indicators also make the data available to process performers. The item “Process metrics are periodically presented to process performers (for e.g. awareness and motivation)” was rated by the firms in the sample as follows:
- 25,33%: No process performance indicators defined
- 18,00%: Disagree
- 22,00%: Neither agree nor disagree
- 34,67%: Agree
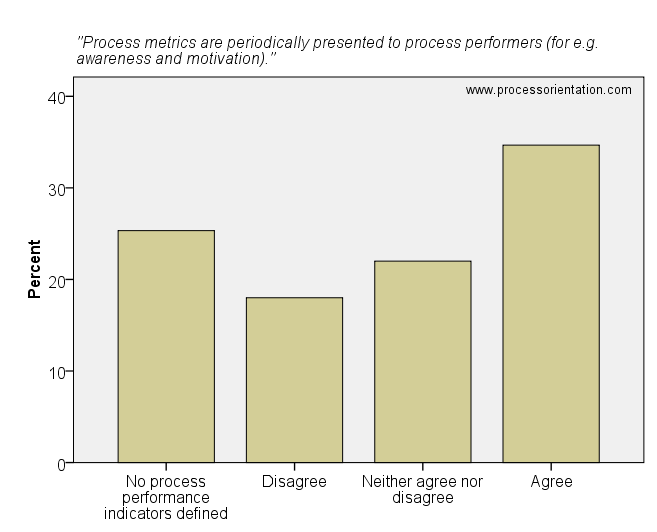
Process metrics are periodically presented to process performers (for e.g. awareness and motivation).
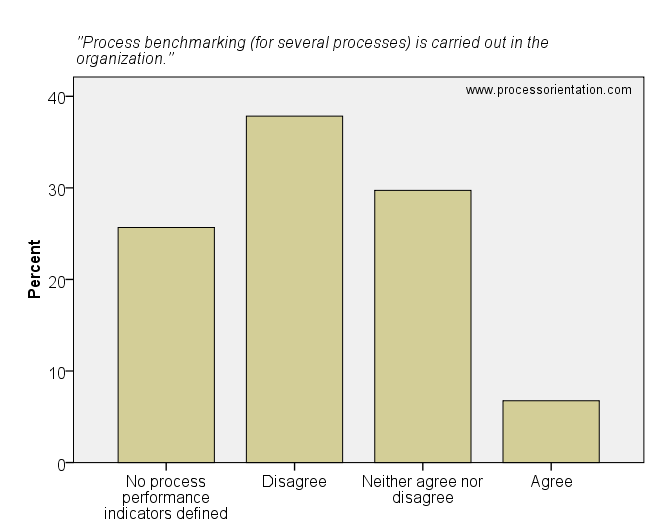
Process benchmarking uses business processes as comparison units and aims to identify best operating practices (Delpachitra and Beal, 2002). The results of the survey reveal that process benchmarking is infrequently used by organizations. The item “Process benchmarking (for several processes) is carried out in the organization” was rated by the firms in the sample as follows:
- 25,68%: No process performance indicators defined
- 37,84%: Disagree
- 29,73%: Neither agree nor disagree
- 6,76%: Agree
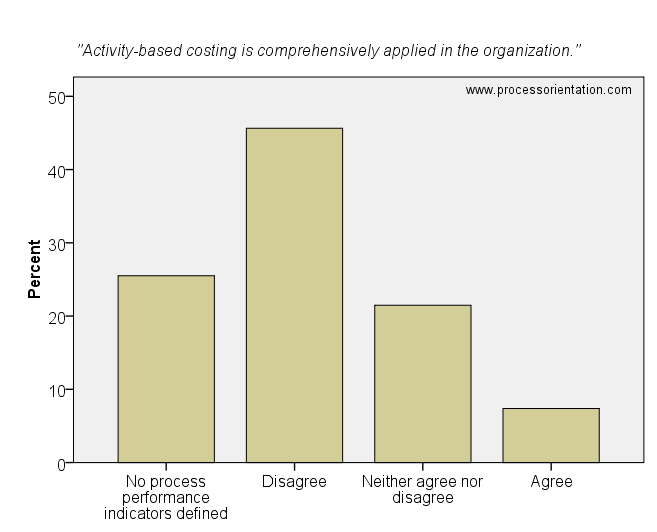
Activity based costing captures costs horizontally in line with business processes (Hinterhuber, 1995). The results of the study reveal that activity based costing is rarely used by organizations. The item “Activity-based costing is comprehensively applied in the organization.” was rated by the firms in the sample as follows:
- 25,50%: No process performance indicators defined
- 45,64%: Disagree
- 21,48%: Neither agree nor disagree
- 7,38%: Agree